SMD Meaning: Guide for Professionals in Electronics
Discover the significance of SMD (Surface-Mounted Device) in electronics with DXM. This page delves into what SMDs are and why they are crucial in modern electronic assemblies. Learn about the advantages of SMDs technology, such as enhanced performance and miniaturization. Explore our insights for a comprehensive understanding of SMD meaning and applications. Stay informed with DXM today.
- What Does SMD Mean in Electronics?
- SMD Meaning and Its Advantages in Electronics
- Key Characteristics of SMDs in Modern Electronics
- Applications of SMDs
- Notes and Warnings
- Benefits of Understanding SMD for Electronics Professionals
- Common Challenges of Working with SMDs
- Enhancing Digital Marketing with SMD Knowledge
- SMD Recommended Soldering Technologies Re-flowing Profile
- Recommended Soldering Technologies of Re-flowing Profile
- SMD Iron Soldering Profile
- Printing Conditions of Solder Paste
- FAQs: Exploring SMD and Its Applications in Electronics
- Conclusion:
- In electronics, SMD meaning refers to "Surface Mount Device," a critical component in modern design. But what does SMD mean, and why is it essential? SMDs technology allows components to mount directly onto PCBs, enhancing efficiency and enabling compact designs. For professionals, understanding SMD meaning ensures optimized space, reduced manufacturing costs, and increased reliability in electronic products.
What Does SMD Mean in Electronics?
The acronym SMD stands for Surface Mount Device. Understanding SMD meaning is crucial in modern electronics, impacting efficiency, size, and cost. It refers to components mounted directly onto a PCB, using Surface Mount Technology (SMT). This technology makes electronic devices more compact, reliable, and cost-effective. Mastering SMDs and their applications helps professionals optimize design and improve manufacturing efficiency, ultimately enhancing product quality and performance.
SMD Meaning and Its Advantages in Electronics
Surface Mount Device, represents a major shift in electronics. Understanding SMD meaning is crucial for professionals. Unlike traditional methods, SMDs are directly placed on a PCB surface, not inserted through drilled holes. This method saves space and supports automation. surface mount device technology allows for smaller, more efficient designs and faster manufacturing processes. The benefits of SMDs include reduced space requirements, increased reliability, and lower production costs, which are vital for modern electronics. Mastering SMDs concepts is essential for optimizing electronic designs and improving overall product efficiency.
Key Characteristics of SMDs in Modern Electronics
Surface Mount Device, is essential in today's electronics. Understanding SMD meaning helps grasp why these components are widely used. Here are the key characteristics of SMDs:
- Compact Design: Small, maximizing space and allowing more components per PCB.
- Enhanced Performance: Shorter paths reduce resistance, enhancing signal speed and performance.
- Types: Common Include resistors, capacitors, diodes, and ICs, with package types like SOIC, QFN, and BGA.
- Advantages: Higher component density and compact designs are ideal for modern electronics like smartphones and tablets.
- Reliability: Sturdy construction ensures durability and prevents detachment during operation.
Mastering SMDs characteristics is crucial for optimizing electronic designs and improving device efficiency.
Applications of SMDs
SMDs are widely employed across various industries:
- Consumer Electronics: From smartphones to wearable tech, SMDs are foundational in crafting compact and efficient products.
- Automotive Electronics: Enhance vehicle functionality with applications in engine control units and infotainment systems.
Medical Devices: Essential for developing compact medical diagnostic tools and monitoring equipment.
Notes and Warnings
The SMDs shall not be operated and stored
under the following environmental condition:
(1) Corrosive or deoxidized atmospheres
(such as chlorine, sulfurated hydrogen, ammonia, sulfuric acid, nitric oxide and so on)
(2) Volatile or inflammable atmospheres
(3) Dusty condition
(4) Excessively high or low pressure condition
(5) Humid site
(6) Places with brine, oil, chemical liquid or organic solvent
(7) Intense vibration
(8) Places with analogously deleterious conditions
The ceramic body of the SMDs is fragile, no excessive pressure or impact shall be exerted on it.
The SMD shall not be operated beyond the specified “Operating Temperature Range” in the catalog.
Choose a proper mounting position that minimize the stress imposedon the chip duringflexing or bending of the board. The recommendationsareshown in the figure below:
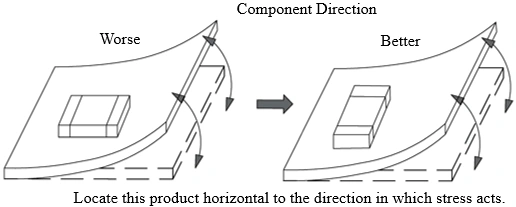
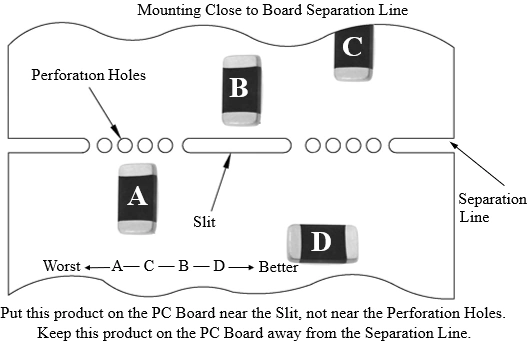
Benefits of Understanding SMD for Electronics Professionals
Understanding Surface Mount Device is crucial in modern electronics. Recognizing SMD meaning provides significant advantages:
- Innovative Design Solutions: Supports creative and complex circuit designs.
- Cost-Effective Production: Reduced materials and automation lower production costs.
- Performance Enhancement: Enables high-speed, high-performance device development.
Knowing SMDs and their impact is vital for professionals aiming for efficiency and innovation in electronic design and production.
Common Challenges of Working with SMDs
Surface Mount Device, offers numerous benefits, but it also presents challenges. Understanding SMD meaning includes recognizing its limitations:
- Precision Requirements: assembly demands high accuracy.
- Repair Difficulty: The small size makes SMDs repair challenging.
While surface mount device has clear advantages, these challenges require careful consideration in the design and production processes.
Enhancing Digital Marketing with SMD Knowledge
Understanding SMD meaning can significantly boost digital marketing for electronics. Sharing valuable content can increase site relevance and user engagement. Educating audiences about surface mount device applications improves search engine visibility, making your website more authoritative and helpful. Leveraging surface mount device knowledge enhances marketing efforts, attracting targeted users and building trust.
The Relationship Between SMD and SMT
Surface Mount Device, relates closely to SMT, Surface Mount Technology. Understanding SMD meaning helps clarify their connection. While SMDs refer to the electronic components, SMT is the method used to mount these components onto PCBs. The adoption of SMT and SMD has revolutionized electronics manufacturing. It enables faster production, lowers costs, and enhances device reliability. Knowing the relationship between SMD and SMT is crucial for professionals aiming to optimize electronic design and production.
SMD Recommended Soldering Technologies Re-flowing Profile
Recommended Soldering Technologies of Re-flowing Profile
→ 1~2℃/sec. Ramp
→ Pre-heating: 150~170℃/90±30 sec.
Insufficient preheating may cause a crack on the ceramic
body. The difference between preheating temperature and
the highesttemperature inthe profileshall be 100℃.
→ Time above 240℃: 20~40 sec.
→ Peak temperature: 260℃ Max./ 10 sec.
→ Solder paste: 96.5wt%Sn/3.0wt%Ag/0.5wt%Cu
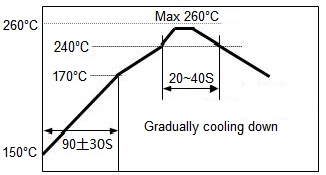
Flux: Use rosin type flux in the soldering process.
If strong acidic flux (with halide content exceeding 0.1wt%) or water-soluble flux(non-rosin type flux including wash-type flux and non-wash-type flux) is used, some problems might be caused in the product characteristics and reliability.
→ Max.2 times for re-flowing.
In case of repeated soldering, the total accumulated soldering time at peak temperatureis within 30sec (Including the first time and second time).
Cooling: Gradual cooling in air. Rapid cooling by dipping in solvent or by other means is not recommended.
Excessive soldering conditions may cause dissolution of metallization or deterioration of solder-wetting on the external electrode.
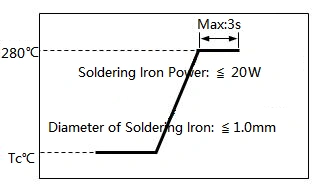
SMD Iron Soldering Profile
Iron soldering power: Max.20W
→ Pre-heating: 150℃/60sec.
→ Soldering Tip temperature: 280℃ Max.
→ Soldering time: 3 sec Max.
→ Solder paste: 96.5wt%Sn/3.0wt%Ag/0.5wt%Cu
→ Max. 1 times for iron soldering
[Note: Take care not to apply the tip ofthe soldering iron to the terminal electrodes.]
Printing Conditions of Solder Paste
The amount of solder is critical . Standard height of fillet is shown in the table below.Too much solder may cause mechanical stress , resulting in cracking of SMD , mechanical and / or electronic damage.
| SMDs Type | Solder Paste Thickness | H of SMD |
| 0201 | 100µm | 1/3T ≤ H ≤ T |
| 0402 | 150µm | 1/3T ≤ H ≤ T |
| 0603, 0805 | 200µm | 0.2mm ≤ H ≤ T |
FAQs: Exploring SMD and Its Applications in Electronics
1.Why are SMDs better than traditional components?
SMDs save space, enhance performance, and improve reliability.
2.Can SMDs be used in high-density applications?
Yes, surface mount devices are ideal for high-density applications like smartphones.
3.What's the primary challenge when working with SMDs?
The main challenge is precision. SMDs assembly demand high accuracy and is hard to repair.
4.What does SMD meaning imply for electronic design?
The SMD meaning implies efficient, compact design that optimizes circuit space.
5.How does SMD affect manufacturing costs?
surface mount device reduces manufacturing costs by allowing automation and using fewer materials.
6.Are SMDs more reliable than through-hole components?
Generally, SMDs offer improved reliability due to stronger connections.
Conclusion:
Knowing SMD meaning can help design cutting-edge technology. Embracing SMDs advantages while managing its challenges is key to staying competitive.
Call to Action: Connect with us to explore surface mount device applications in your projects. Effectively using SMD leads to innovation and better production efficiency.
In conclusion, SMDs play a vital role in modern electronics, enhancing design efficiency and streamlining manufacturing processes. Engage with us to discover how it can drive your project’s success.
© 2024 DXM Blog. All rights reserved.
Author: Ivan Huang
Recommended for you

Resistance Heating & Heater: A Guide for Professionals

Understanding Thermistor: A Comprehensive Guide

Coolant Temp Sensor – Expert Maintenance Tips

Temp.Sensor: A Guide to Ensuring Accurate Engine Performance

Positive Temperature Coefficient Sensor : A Comprehensive Guide

What Are NTC Thermistors Made Of ? Discover the Secrets
Logistics
Is your logistics and distribution service reliable?
Yes, we cooperate with a number of well-known logistics companies to ensure the timeliness and reliability of logistics and distribution services and provide you with a satisfactory distribution experience.
Does your product support global logistics and distribution?
Yes, our products support global logistics and distribution services, and you can receive our products anytime and anywhere.
How long does logistics delivery take?
Shipping times depend on your location and the shipping method you choose. Generally speaking, international shipping can take anywhere from a few weeks to a few months.
Price and Payment
How are the prices of your products determined?
Our product prices are based on a variety of factors, including order quantity, customization requirements, and market competition.
What’s the Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) and Minimum Order Amount (MOA)
MOQ: 10000PCS
You may also like

KTY83-110 Sensor with Silicon Glass Thermistor

Bracket Type NTC Thermal Sensor MF52X for Precise Temperature Measurement

Glass Thermistors MF58E for High-Precision Applications

High Precise NTC Sensors for Temperature Measurement and Control

WMZ12A 75S PTC Thermistors for Over-Current and Over-Load Protection

SMD Sensors: Advanced Temperature Sensing Excellence

Thermistor PTC MZ11 Series for Light Efficient Design

PTC Thermistors for Ballast Electronic and Energy Saving Lighting Intelligent Preheat Start MZ12 | DXM
Get in Touch
Discover premium thermistors, sensors, and resistors tailored to your needs.Our dedicated team of experts is available to assist with product selection, technical queries, and after-sales service. Contact us for custom solutions and experience exceptional customer support.
© 2024 DXM | Designed by gooeyun

 Scan QR Code
Scan QR Code
Scan QR Code
Whatsapp: +8618927361658
Shenzhen DXM Technology Co., Ltd.
DXM PTCNTC
Shenzhen DXM Technology Co., Ltd