What is a Temperature Probe?
A temperature probe is a tool used to measure temperature in various environments, providing precise and reliable data for process control, safety, and efficiency. These probes come in different designs, each tailored for specific applications such as industrial processes, medical devices, or food safety. By understanding the types and how they operate, businesses can optimize their processes and ensure accurate readings. Knowing how a temperature probe works is critical to selecting the right one for your needs.
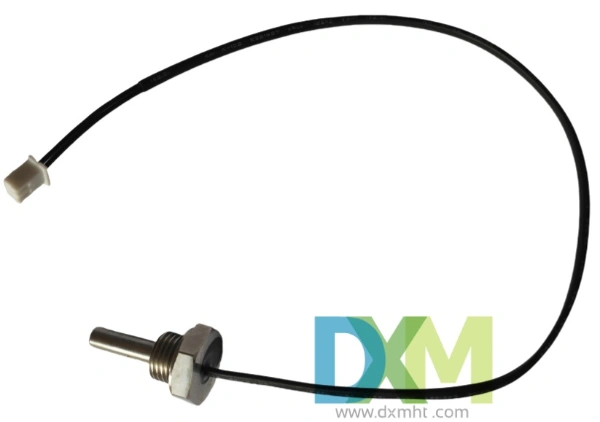

The Role of Temperature Probe in Industrial Applications
In industries ranging from food processing to pharmaceuticals, temperature probes are crucial for ensuring product quality, safety, and operational efficiency. Without these devices, it would be nearly impossible to maintain strict temperature control over various processes. For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, maintaining the right temperature for drug storage is critical for ensuring the efficacy and safety of medications. Similarly, in manufacturing, controlling the temperature during metalworking processes can significantly impact the quality of the final product.
Types of Temperature Probes
There are several types of temperature probes, each suitable for different temperature ranges and environments. The most common types include:
Thermocouples
Thermocouples are one of the most widely used types of temperature probes. They work on the Seebeck effect, where two dissimilar metals generate a voltage proportional to the temperature difference. Thermocouples are known for their durability and ability to measure a wide range of temperatures, making them ideal for high-temperature applications such as furnaces or kilns. Because of their cost-effectiveness, thermocouples are found in applications ranging from industrial processes to everyday appliances.
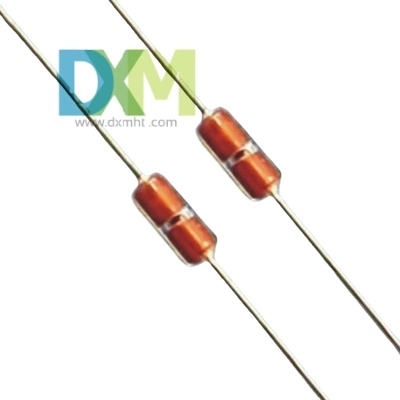
Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs)
RTDs are highly accurate probes that use the principle that a material's electrical resistance changes with temperature. Platinum RTDs are particularly common due to their stability and accuracy. RTDs are ideal for precision measurements in industries like pharmaceuticals and scientific research. The accuracy and stability of RTDs make them a preferred choice when the highest precision is required, such as in temperature-controlled environments in laboratories and research facilities.
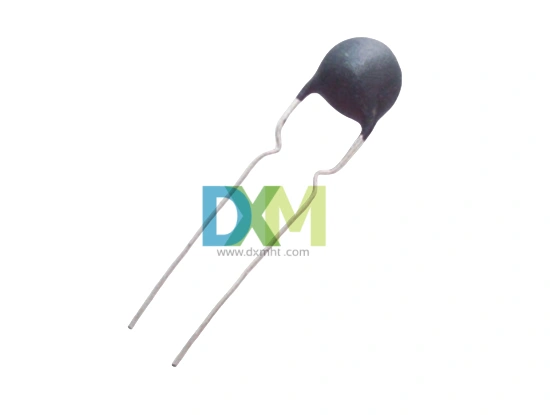
Thermistors
Thermistors are made of semiconductor materials and have a high sensitivity to temperature changes. They are ideal for precise temperature measurement over a narrow range. While thermistors are cost-effective, they tend to have lower stability compared to RTDs and thermocouples. However, they are frequently used in consumer electronics and medical devices, where precise measurements in a small range are required, such as body temperature sensors in medical applications.
Infrared (IR) Temperature Probe
Unlike contact probes, infrared temperature probe measures temperature without direct contact by detecting infrared radiation. This makes it suitable for hazardous or moving objects in applications like food processing or building inspections. The non-contact feature of infrared probes ensures that it can measure temperature in environments where traditional probes may not be applicable due to high risks or movement.
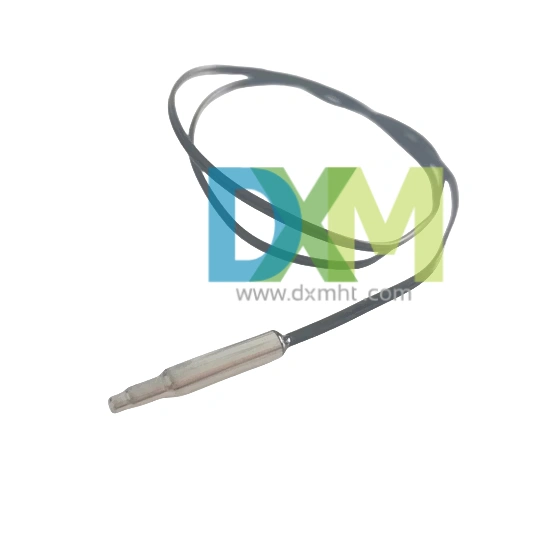
Fiber Optic Temperature Probe
Fiber optic temperature probe is used in environments where electrical probes cannot be employed due to the presence of electrical noise or extreme conditions. This probe is known for its high accuracy and ability to function in harsh environments. Fiber optic probes are commonly used in aerospace, nuclear power plants, and in other critical infrastructure environments where temperature accuracy is essential, and electrical interference could compromise readings.
Choosing the Right Temperature Probe
Choosing the right temperature probe is critical to ensure accurate and reliable measurements. Here are key factors to consider:
- Temperature Range: Ensure the probes cover the expected temperature range of your application. Different temperature probes have varying ranges, from extreme high temperatures to lower ranges suitable for medical applications.
- Accuracy: The probe’s accuracy is crucial, especially in precision-driven industries like pharmaceuticals or semiconductor manufacturing.
- Response Time: Consider the speed at which the probes respond to temperature changes. In some applications, rapid response time is essential for process control.
- Environment: The probe’s construction must withstand environmental factors like moisture, pressure, and corrosive substances. A temperature probe designed for industrial environments will likely have different requirements than one for use in medical devices.
- Application: The intended application may dictate the type and features of the probe required. For example, a temperature probe used in food processing needs to meet different standards than one used in chemical production.
- Budget: Consider both the initial cost of the probe and any ongoing maintenance or calibration costs.
Maintenance and Calibration of Temperature Probes
Regular maintenance and calibration are crucial for ensuring that temperature probes continue to provide accurate readings. Calibration should be performed regularly, based on the application’s needs and industry standards. Neglecting calibration can result in inaccurate measurements, potentially leading to process inefficiencies or safety risks. In critical applications, such as pharmaceutical or food processing, frequent calibration is necessary to maintain compliance with industry regulations.
Applications of Temperature Probe Across Industries
Temperature probes are vital in a variety of industries. Here are some key areas where temperature probes play an essential role:
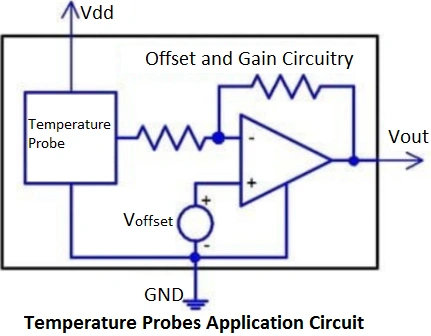
- Food and Beverage: Ensuring safety and quality control during processing and storage.
- Pharmaceuticals: Maintaining optimal temperature conditions for drug manufacturing and storage.
- HVAC: Monitoring temperatures to ensure efficient and comfortable building climates.
- Manufacturing: Temperature control in processes like metalworking, plastics, and semiconductor production.
- Environmental Monitoring: Measuring temperature for climate research and weather forecasting.
- Medical: Used for patient monitoring and calibration of medical equipment.














 Scan QR Code
Scan QR Code
Scan QR Code
Whatsapp: +8618927361658
Shenzhen DXM Technology Co., Ltd.
DXM PTCNTC
Shenzhen DXM Technology Co., Ltd