Heat Probe & Heat Sensing: A Complete Guide
Learn about comprehensive guide on heat probe and heat sensing technology, presented by DXM. This article delves into the intricacies of heat probes and their applications in various industries, ensuring precision and efficiency. Enhance your understanding of heat sensing techniques for optimized performance. Explore now for authoritative insights.
- What is a Heat Probe?
- Types of Heat Probe
- 1. Thermocouple Heat Probe
- 2. Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs)
- 3. Thermistor and Its Applications
- 4. Infrared Heat Probe
- Applications of Heat Probe and Sensing Technology
- 1. Industrial Applications
- 2. Food Safety and Quality Control
- 3. Medical and Pharmaceutical Applications
- 4. Environmental Monitoring
- Choosing the Right Heat Probe for Your Needs
- The Future of Heat Sensing Technology
- Conclusion
- Call to Action
In industries that require precise temperature control, a heat probe is an essential tool. From food processing to manufacturing, heat sensing technologies have transformed how we monitor and manage temperatures. Whether you're in a lab, a factory, or even at home, understanding how these tools work can improve efficiency and safety.
This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about heat probe and heat sensing technologies. We will dive deep into their various types, applications, and how they are revolutionizing the way we approach temperature monitoring. Throughout this guide, we will focus on two key concepts: heat probe and heat sensing technologies, which are at the heart of many industrial, scientific, and commercial applications.
What is a Heat Probe?
A heat probe is a device that detects and measures temperature by sensing the heat emitted from an object or substance. The measurement is then translated into data that can be used for various applications. Heat sensing refers to the technology used to capture this heat and translate it into accurate readings. The heat probe can be used in a range of applications, from ensuring food safety to optimizing industrial processes.
Heat probe can either be in direct contact with the object they are measuring, or it can use non-contact methods such as infrared (IR) sensing. The latter type of probe is often used in situations where direct contact would be impractical or dangerous.
In simple terms, heat sensing is the process of measuring and interpreting temperature variations using specific tools—heat probe being one of the most fundamental. This technology is integral to maintaining optimal conditions in industrial, scientific, and everyday settings.
Types of Heat Probe
1. Thermocouple Heat Probe
Thermocouples are among the most common heat probe due to its robustness, versatility, and affordability. This heat probe works by measuring the voltage difference generated when two different metals are joined together. When heated, these metals produce a voltage that correlates with the temperature difference.
Thermocouple heat probe is widely used in industries where high temperatures are common, such as in furnace monitoring, kiln operation, and high-temperature manufacturing. This heat probe can withstand temperatures of up to 1,000°C, making it ideal for extreme environments. its reliability in fluctuating temperature conditions also makes it an essential tool in scientific experiments that require real-time temperature readings.
The key advantage of thermocouples lies in their ability to operate over a broad temperature range, making them versatile for many applications. Thermocouple heat sensing systems are ideal for industries that need a simple, cost-effective way to measure temperature.
2. Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs)
RTDs are another type of heat probe that operates based on the principle of electrical resistance. RTDs are made of materials, typically platinum, whose resistance increases with temperature. This change in resistance is used to determine the temperature of an object or substance.
RTDs provide more accurate temperature readings compared to thermocouples, making them the preferred choice for high-precision temperature sensing applications. Industries such as pharmaceuticals, food safety, and electronics often use RTDs to ensure temperature control within specific tolerances.
In terms of heat sensing, RTDs are highly reliable and provide precise temperature readings in ranges typically from -200°C to 850°C. They offer better long-term stability and are especially valuable in environments where maintaining precise temperature control is essential.
3. Thermistor and Its Applications
Thermistor is heat probe that is specifically designed to measure temperature by detecting changes in electrical resistance. It differs from RTDs in that it provides a greater sensitivity to temperature changes over a smaller range. Thermistor is often used for precise temperature measurements in controlled environments, such as in medical devices, HVAC systems, and automotive applications.
The primary advantage of thermistor over other heat probe is its high sensitivity to temperature changes, making it ideal for applications where small fluctuations in temperature need to be detected. However, its relatively narrow temperature range (compared to thermocouples or RTDs) means it is less versatile in extreme conditions.
4. Infrared Heat Probe
Infrared (IR) heat probe represents a major advancement in heat sensing technology. Unlike other heat probes that require physical contact with the object being measured, IR heat probe uses infrared radiation to detect the temperature of an object without touching it. The emitted infrared radiation is directly related to the object's temperature, which is then converted into an accurate temperature reading.
This type of heat probe is ideal for measuring temperatures in environments where direct contact with the object would be hazardous or difficult. Applications include measuring the temperature of moving objects, hazardous materials, or heated surfaces in hard-to-reach areas.
Applications of Heat Probe and Sensing Technology
The applications of heat probe and heat sensing technologies are vast and varied. These tools are used across many industries to ensure temperature control, safety, and operational efficiency.
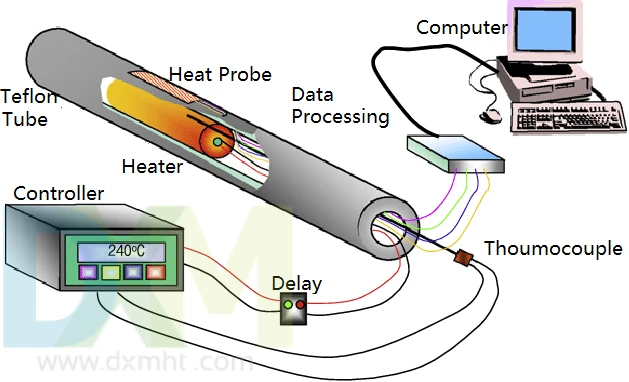
1. Industrial Applications
In industrial settings, maintaining precise temperature control is critical to ensuring the quality of the final product and the safety of operations. Heat probes are used extensively in manufacturing environments, especially in metal processing, chemical production, and power generation. These industries rely on heat sensing technologies to monitor furnace temperatures, cooling processes, and equipment performance.
Heat probe can be installed in various parts of a system to provide real-time data on temperature fluctuations. This data can then be used to adjust processes dynamically, ensuring that it remains within optimal operating conditions. For instance, in chemical production, precise temperature control can impact reaction rates, product quality, and energy efficiency.
2. Food Safety and Quality Control
In the food industry, heat probes play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and quality of products. By monitoring the temperature of cooking, cooling, and storage processes, heat sensing technologies help to reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses.
For example, in the preparation of cooked food, heat probe is used to ensure that meats are cooked to a safe internal temperature. Similarly, in the refrigeration of perishable goods, heat sensing technology ensures that storage temperatures are maintained to prevent spoilage.
3. Medical and Pharmaceutical Applications
In the medical field, temperature control is essential, particularly when storing and transporting sensitive biological materials like vaccines or blood. Heat probes are used to monitor storage conditions and ensure compliance with strict temperature requirements. Temperature sensors are also integral to devices such as incubators, which maintain precise environments for biological research and medical procedures.
The pharmaceutical industry also benefits from heat sensing technologies in the manufacturing process, where precise temperature control is required to ensure the stability and efficacy of medications. Whether it's in drug production or the transportation of sensitive products, heat probe helps maintain the necessary conditions.
4. Environmental Monitoring
Environmental monitoring systems often rely on heat probes to gather data on temperature changes in outdoor and indoor environments. For example, in climate research, heat sensing systems can track temperature changes in ecosystems, providing valuable insights into climate change patterns. Similarly, heat probe is used in construction to monitor temperatures in buildings and ensure that HVAC systems are functioning properly.
Choosing the Right Heat Probe for Your Needs
When selecting a heat probe, several factors must be considered to ensure that the right tool is chosen for the application. These factors include the temperature range, accuracy, response time, and environmental conditions.
For applications that require high precision, an RTD or thermistor heat probes may be the best option. However, for industries where temperatures fluctuate rapidly or reach extremely high levels, thermocouples are likely the better choice. Additionally, for situations where contact with the object being measured is not possible or safe, infrared heat probes provide an ideal solution.
The Future of Heat Sensing Technology
As industries continue to evolve and demand for more precise temperature control increases, heat sensing technologies will continue to advance. The future of heat probe lies in the development of even more sensitive and accurate sensors, as well as the integration of these technologies into automated systems. Wireless heat sensing and data logging will also become more prevalent, enabling real-time monitoring and remote access to temperature data.
Moreover, as industries become more focused on energy efficiency and sustainability, the role of heat probes in optimizing temperature management will be essential. By providing more accurate temperature readings, businesses can reduce energy consumption, lower costs, and enhance operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Heat probe and heat sensing technologies are indispensable tools in modern industry, healthcare, and research. With a variety of options to suit different needs, these devices provide precise temperature readings that are crucial for safety, efficiency, and quality control. As technology continues to evolve, the role of heat probes in industrial and scientific applications will only become more critical, and the integration of advanced heat sensing features will help improve performance and reduce costs.
For any industry or application that requires temperature control, selecting the right heat probe is key to achieving optimal results. Whether for manufacturing, food safety, or medical use, these technologies are shaping the future of temperature measurement and control.
Call to Action
If you’re ready to explore the world of heat probe and heat sensing technologies, visit our product page for more information. Our range of heat probes.
© 2025 DXM Blog. All rights reserved.
Author: Ivan Huang
Recommended for you

Water Temperature Sensor: The Key to Engine Health and Efficiency

Lightning Surge Protection Varistor: Essential for Protecting Your Electrical Systems

Water Temp Sensor: How to Test it for Reliable Performance?
Capacitor Impedance: Calculation Guide & FAQs

Temperature Probe Sensor: A Comprehensive Guide

Termistor NTC: What Does a Thermistor Do?
Logistics
Does your product support global logistics and distribution?
Yes, our products support global logistics and distribution services, and you can receive our products anytime and anywhere.
How long does logistics delivery take?
Shipping times depend on your location and the shipping method you choose. Generally speaking, international shipping can take anywhere from a few weeks to a few months.
Can I change my shipping address?
Yes, you can contact our customer service team to modify the delivery address before order confirmation to ensure that the order can be accurately delivered to the address you specify.
How to track my order?
You can track your order through our official website or the order number provided and learn about the logistics status and delivery progress of your order at any time.
Customized Services
Free sample availability
You can contact our representative via email, fax or phone to specify the sample you need and provide your courier's account number (such as UPS, FedEx, DHL, TNT, etc.).. And we’ll send you samples free of charge through your courier by freight collection.
You may also like

KTY83-110 Sensor with Silicon Glass Thermistor

Bracket Type NTC Thermal Sensor MF52X for Precise Temperature Measurement

Glass Thermistors MF58E for High-Precision Applications

High Precise NTC Sensors for Temperature Measurement and Control

WMZ12A 75S PTC Thermistors for Over-Current and Over-Load Protection

SMD Sensors: Advanced Temperature Sensing Excellence

Thermistor PTC MZ11 Series for Light Efficient Design

PTC Thermistors for Ballast Electronic and Energy Saving Lighting Intelligent Preheat Start MZ12 | DXM
Get in Touch
Discover premium thermistors, sensors, and resistors tailored to your needs.Our dedicated team of experts is available to assist with product selection, technical queries, and after-sales service. Contact us for custom solutions and experience exceptional customer support.
© 2024 DXM | Designed by gooeyun

 Scan QR Code
Scan QR Code
Scan QR Code
Whatsapp: +8618927361658
Shenzhen DXM Technology Co., Ltd.
DXM PTCNTC
Shenzhen DXM Technology Co., Ltd