Choose the Right Thermistor for Your Inrush Current Protection
Explore the differences between NTC and PTC thermistors for effective inrush current limitation in our latest article at DXM. Delve into the advantages of NTC thermistors in preventing circuit overloads and compare them with PTC thermistors. Enhance your understanding of how these essential thermistor components optimize electrical systems. Whether you're choosing thermistor for engineering projects or industrial applications, our insights will guide you. Discover more about thermistor technology today and stay ahead with DXM.
- Protect Your Devices from Inrush Current with Thermistor
- How NTC and PTC Thermistors Control Inrush Current
- NTC vs PTC Thermistors: Which One to Choose?
- Why Controlling Inrush Current is Important
- How Thermistor Protects Electrical Systems from Inrush Current
- NTC vs PTC Thermistor: What's the Difference?
- Why Thermistor Is Key for Device Longevity?
- NTC Thermistors: Effective Solutions for Temperature and Current Control
- How NTC Thermistors Work
- Applications of NTC Thermistors Across Industries
- PTC Thermistors: Fast Protection Against Overcurrent
- How PTC Thermistors Operate
- Applications of PTC Thermistors
- The Great Debate: Thermistor for Inrush Current Protection
- When to Choose NTC Thermistors
- When to Choose PTC Thermistors
- NTC vs PTC Thermistor: Which Is Right for You?
- Conclusion: Choosing the Right Thermistor for Inrush Current Protection
Protect Your Devices from Inrush Current with Thermistor
How NTC and PTC Thermistors Control Inrush Current
Both NTC Thermistors (Negative Temperature Coefficient) and PTC Thermistors (Positive Temperature Coefficient) provide effective control of inrush current. NTC thermistors decrease resistance as they heat up, allowing for a gradual flow of current. PTC thermistors, by contrast, increase resistance to limit excessive current during surges.
NTC vs PTC Thermistors: Which One to Choose?
Choosing between NTC thermistors and PTC thermistors depends on your system's requirements. NTC thermistors are ideal for applications needing gradual current control, while PTC thermistors work best for overcurrent protection. Knowing the difference between ntc vs ptc thermistor is key to selecting the right solution.
Why Controlling Inrush Current is Important
Uncontrolled inrush current can damage your devices, much like how light bulbs often burn out when turned on. By using NTC or PTC thermistors, you safeguard your equipment, reduce stress on components, and ensure longer operational life.
Incorporating thermistors into your systems protects your devices from electrical surges, minimizes wear, and helps avoid costly downtime.
How Thermistor Protects Electrical Systems from Inrush Current
Thermistor is essential for managing inrush current and protecting electrical systems. This small, efficient device changes its resistance based on temperature. The two primary types used for inrush current control are NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient) thermistors and PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) thermistors. Though both help manage current surges, they function differently and suit various applications.
NTC Thermistors reduce their resistance as temperature increases, allowing a smooth current flow as the device powers up. In contrast, PTC Thermistors increase resistance as current rises, limiting excessive current and protecting circuits.
NTC vs PTC Thermistor: What's the Difference?
Choosing between NTC and PTC thermistors depends on your system’s needs. NTC thermistors are ideal for applications where gradual current flow is needed. PTC thermistors, however, are better suited for overcurrent protection. Understanding ntc vs ptc thermistor features will guide you in selecting the right component.
Why Thermistor Is Key for Device Longevity?
By managing inrush current, NTC thermistors and PTC thermistors prevent damage to electrical systems. These components help extend device lifespan, reduce stress on components, and enhance reliability.
Incorporating thermistor into your designs ensures protection from current surges, helping your devices operate efficiently and last longer.
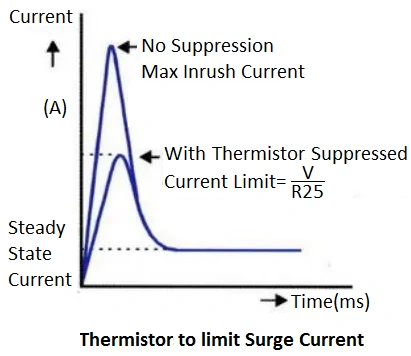
NTC Thermistors: Effective Solutions for Temperature and Current Control
How NTC Thermistors Work
NTC Thermistors (Negative Temperature Coefficient) operate by decreasing resistance as temperature rises. Initially, when power is applied, they offer high resistance, limiting the flow of current. As they heat up from the current, their resistance drops, allowing the system to function normally.
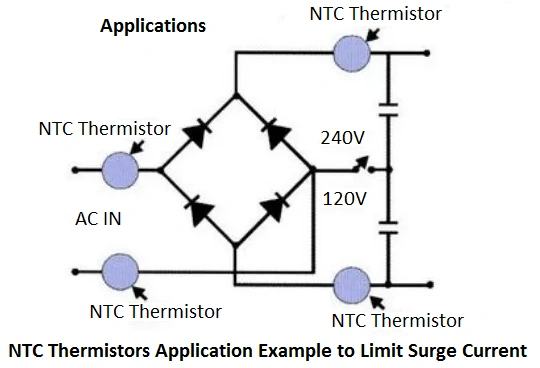
Applications of NTC Thermistors Across Industries
NTC Thermistors are versatile and widely used in various industries due to their efficiency:
- Automotive: Crucial for engine temperature monitoring and battery management systems.
- Household Appliances: Used in devices like ovens and refrigerators for precise temperature regulation.
- Industrial Equipment: Commonly found in process control systems and HVAC for stable operations.
Their ability to deliver accurate temperature readings makes NTC thermistor essential for a wide range of electronic devices.
By incorporating NTC thermistor into these systems, manufacturers ensure optimal performance and device longevity.
Recommended for you

Water Temperature Sensor: The Key to Engine Health and Efficiency

Lightning Surge Protection Varistor: Essential for Protecting Your Electrical Systems

Water Temp Sensor: How to Test it for Reliable Performance?
Capacitor Impedance: Calculation Guide & FAQs

Temperature Probe Sensor: A Comprehensive Guide

Termistor NTC: What Does a Thermistor Do?
Logistics
Does your product support global logistics and distribution?
Yes, our products support global logistics and distribution services, and you can receive our products anytime and anywhere.
Is your logistics and distribution service reliable?
Yes, we cooperate with a number of well-known logistics companies to ensure the timeliness and reliability of logistics and distribution services and provide you with a satisfactory distribution experience.
Does it support express delivery?
Yes, we support express delivery services. You can choose different delivery methods according to your needs, including ordinary express delivery and expedited express delivery.
Shipment
1)Small order quantity and small packing:cargo may be arranged by courier;
2)Bulk order and big volume:shipment may be arranged by sea or by air as per customer’s requirements on FOB, C&F,CIF or LCL terms and do prompt shipment which is very important for our customers, so we do this matter seriously and we may arrange our shipment in time due to our rich experiences in this line. We may also accept the shipment on the term of freight prepaid or freight collect.
Price and Payment
Do you offer bulk purchase discounts?
Yes, we offer bulk purchase discounts; the specific discount rate depends on the order quantity and cooperation method.
You may also like

KTY83-110 Sensor with Silicon Glass Thermistor

Bracket Type NTC Thermal Sensor MF52X for Precise Temperature Measurement

Glass Thermistors MF58E for High-Precision Applications

High Precise NTC Sensors for Temperature Measurement and Control

WMZ12A 75S PTC Thermistors for Over-Current and Over-Load Protection

SMD Sensors: Advanced Temperature Sensing Excellence

Thermistor PTC MZ11 Series for Light Efficient Design

PTC Thermistors for Ballast Electronic and Energy Saving Lighting Intelligent Preheat Start MZ12 | DXM
Get in Touch
Discover premium thermistors, sensors, and resistors tailored to your needs.Our dedicated team of experts is available to assist with product selection, technical queries, and after-sales service. Contact us for custom solutions and experience exceptional customer support.
© 2024 DXM | Designed by gooeyun

 Scan QR Code
Scan QR Code
Scan QR Code
Whatsapp: +8618927361658
Shenzhen DXM Technology Co., Ltd.
DXM PTCNTC
Shenzhen DXM Technology Co., Ltd