Heating Elements: Understanding Types, Applications, and Selection Guide
Discover the essential insights into heating elements with DXM's comprehensive guide. Explore various types and applications to make informed choices for your needs. Our selection guide ensures you find the perfect heating element solution. Trust DXM for reliable and efficient heating part, tailored for optimal performance and longevity. Enhance your knowledge and make the right decision with our expert guidance.
- Types of Heating Elements
- 1. Metal Heating Element
- 2. Ceramic and Semiconductor Heating Element
- 3. Thick Film Heating Elements
- 4. Polymer PTC Heating Element
- 5. Composite Heating Element
- 6. Quartz Halogen Heating Elements
- Applications of Heating Elements
- Factors to Consider When Selecting a Heating Element
- 1. Material Properties
- 2. Wattage Requirements
- 3. Design and Configuration
- Advantages of Using Different Heating Elements
- 1. Energy Efficiency
- 2. Durability and Reliability
- 3. Versatility
- Summary
- FAQs Section
- Q1: What are heating elements, and how do they work?
- Q2: What materials are commonly used for heating elements?
- Q3: How do I choose the right heating element?
- Q4: What are the main applications of heating elements?
- Q5: What is the advantage of using polymer PTC heating element?
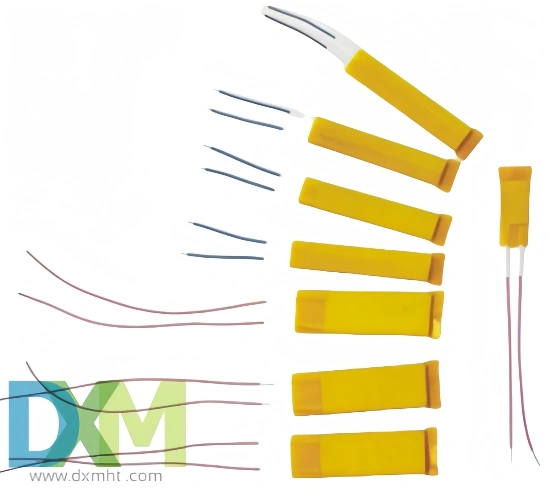

Heating elements convert electrical energy into heat through Joule heating. When current passes through a heating element, it encounters resistance, generating heat.Heating elements are vital in household appliances and industrial systems. They provide efficient heat management for various sectors.Choosing the right type depends on understanding materials and application needs. This guide explores different heating elements, their uses, selection factors, and material advantages.Selecting the proper heating part can improve efficiency and longevity, making it crucial for industrial and residential heating solutions.
Types of Heating Elements
1. Metal Heating Element
Metal heating element is some of the most common types of heating elements available, due to their versatility and efficiency. This heating element is composed of various metal alloys that offers different levels of resistance and thermal conductivity, making it suitable for a wide range of applications:
- Nickel-Chromium (NiCr): Known for its high melting point and resistance to oxidation, making it ideal for high-temperature applications such as furnaces, industrial ovens, and toasters. Nickel-chromium heating elements are capable of withstanding prolonged exposure to high temperatures without breaking down, providing durability and reliability in demanding environments.
- Copper-Nickel (CuNi): This element has low resistivity and excellent corrosion resistance, suitable for low-temperature heating systems like electric blankets, hot water immersion heaters, and space heaters. The combination of copper and nickel creates an alloy that is resistant to oxidation and retains its properties even at elevated temperatures, making it suitable for household and industrial applications alike.
2. Ceramic and Semiconductor Heating Element
Ceramic-based heating element is ideal for stable heating requirements. This heating element is known for its quick response time and its ability to maintain consistent temperatures over long periods of operation:
- Sealed Ceramic: Fast heating and high heat retention make sealed ceramic heating element suitable for long-duration heating applications, such as space heaters, radiant heaters, and ovens. These elements are durable and capable of maintaining stable temperatures for extended periods, ensuring efficient and even heat distribution.
- Silicon Carbide: Operates at very high temperatures and is often used in the glass manufacturing industry and metal treatment processes. Silicon carbide heating element can reach temperatures of up to 1600°C, making them ideal for applications where extreme heat is necessary, such as kilns, furnaces, and glass production.
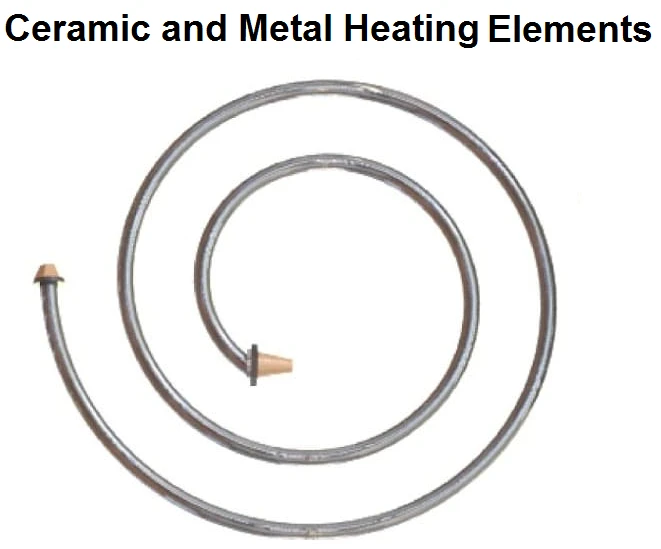

3. Thick Film Heating Elements
Printed on substrates, thick film heating elements provide advantages such as low thermal mass, fast response, and high power density. These elements are widely used in medical devices, automotive systems, and precision heating applications due to their efficient design and ability to provide targeted heating. The versatility of thick film heating element makes them suitable for heating fluids, gases, and surfaces in a variety of industries. The compact size and high efficiency of these heating elements contribute to their popularity in applications where space is limited.
4. Polymer PTC Heating Element
Polymer Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) heating element is self-regulating and made from materials like silicone rubber mixed with conductive particles. This heating element adjusts its resistance based on temperature changes, making it safe and energy-efficient. The ability of polymer PTC heating element to self-regulate means it is often used in applications such as electric radiators, heated seating, and underfloor heating systems. Polymer PTC heating elements can prevent overheating and improve safety, as their resistance increases with temperature, reducing power consumption once the desired temperature is reached.
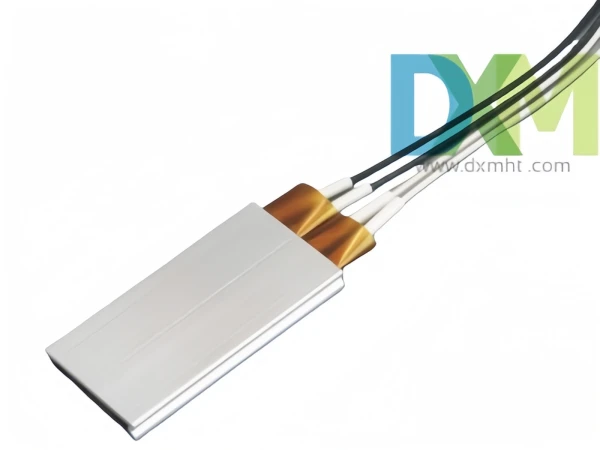

5. Composite Heating Element
Composite heating element combines different materials to enhance performance. This heating element is often custom-designed for specific purposes such as chemical manufacturing, where resistance to harsh environments is essential. Composite heating part is used in processes requiring precise temperature control, such as chemical synthesis and specialized industrial equipment. By combining different materials, manufacturers can create heating element with optimized thermal properties, tailored to meet the specific needs of an application.
6. Quartz Halogen Heating Elements
Quartz halogen heating elements are known for their rapid heating and cooling capabilities, making them perfect for applications that require quick temperature changes. These heating elements are commonly used in laboratory testing equipment, infrared heating systems, and industrial dryers. Quartz halogen heating part produces radiant heat, which is highly efficient and can be directed precisely where needed. This makes it ideal for drying coatings, curing adhesives, and conducting temperature-sensitive experiments.
Applications of Heating Elements
Heating elements are used in many everyday applications, providing efficient heat across industries.
Household Appliances: Devices like ovens, toasters, kettles, and dryers rely on heating element for consistent, efficient heating. This element ensures reliable heat for cooking, boiling, and drying needs.
Industrial Processes: Heating element is crucial in sintering ceramics, curing rubber, and treating metals. High-power elements, like silicon carbide and nickel-chromium, provide precise temperature control in manufacturing.
Specialized Equipment: Medical devices, automotive heating, and laboratory tools often use specialized heating elements. Thick film elements maintain temperatures in medical devices, while ceramic elements help with defrosting and regulation in automotive systems.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Heating Element
1. Material Properties
The choice of material for a heating element affects its operating temperature range, durability, and resistance to corrosion. For high-temperature applications, materials like nickel-chromium are ideal due to their resistance to oxidation and ability to withstand prolonged exposure to heat. On the other hand, polymer PTC heating elements are ideal for moderate heating applications where energy efficiency and self-regulation are important considerations.
2. Wattage Requirements
Wattage requirements depend on the specific heating needs of the application. Selecting the appropriate wattage is crucial for ensuring efficient and effective heating. Higher wattage heating element provides faster heating but must be chosen carefully to avoid safety risks or energy inefficiency. In applications like ovens or furnaces, high-wattage heating part is necessary to achieve the required temperatures, while low-wattage heating elements are sufficient for applications like heated seating or underfloor heating.
3. Design and Configuration
Choosing the right design and configuration for a heating element is essential for achieving optimal performance. The shape, size, and placement of the heating element must be suitable for the intended application. Tubular heating elements, for example, are commonly used in water heaters and immersion heaters, where the tubular design allows for even heat distribution throughout the water. Flat heating elements, such as thick film heaters, are ideal for providing targeted heating in appliances like electric griddles and induction cooktops.
Advantages of Using Different Heating Elements
1. Energy Efficiency
One of the key advantages of modern heating element is its energy efficiency. Heating part likes polymer PTC and quartz halogen element is designed to provide maximum heat output with minimal energy consumption. By selecting the appropriate heating part for a specific application, energy usage can be optimized, reducing costs and improving overall efficiency.
2. Durability and Reliability
The durability of heating elements depends largely on the materials used in their construction. Nickel-chromium and silicon carbide heating element is known for its ability to withstand high temperatures and resist oxidation, ensuring a longer service life. This durability is crucial in industrial applications, where equipment downtime can result in significant costs and production delays.
3. Versatility
Heating elements come in a variety of shapes, sizes, and materials, making them suitable for numerous applications. From household appliances to industrial machinery, the versatility of heating element makes it an integral component in a wide range of heating solutions. This adaptability allows manufacturers to design custom heating solutions that meet the specific requirements of each application.
Summary
Heating elements are critical in many applications, effectively converting electrical energy into heat. From nickel-chromium elements for high temperatures to polymer PTC elements, heating elements offer diverse solutions. Selecting the right heating part depends on material, design, and wattage for efficient results.
Understanding different heating elements, their uses, and performance factors ensures the best choice for your needs. Whether for industrial furnaces, household appliances, or medical devices, the right heating element enhances efficiency and reliability.
FAQs Section
Q1: What are heating elements, and how do they work?
A: Heating elements convert electrical energy into heat through Joule heating, where the resistance to electric current generates heat. They are used in many applications, from household appliances to industrial equipment, to provide efficient and controlled heating.
Q2: What materials are commonly used for heating elements?
A: Common materials include nickel-chromium alloys, copper-nickel alloys, ceramics, silicon carbide, and polymers. The choice of material depends on the required temperature, durability, and application. Nickel-chromium is suitable for high-temperature applications, while polymer PTC elements are used in applications requiring self-regulation and safety.
Q3: How do I choose the right heating element?
A: Consider factors like the required operating temperature, wattage, material properties, and the application. High-temperature applications need durable materials like nickel-chromium, while self-regulating elements like polymer PTC are ideal for moderate heating needs. Ensuring the correct wattage and configuration is also critical for achieving efficient heating.
Q4: What are the main applications of heating elements?
A: Heating elements are used in household appliances (ovens, kettles, clothes dryers), industrial processes (metal treatment, ceramic sintering, rubber curing), and specialized equipment (medical devices, automotive heating, laboratory testing). Their ability to provide consistent and controlled heating makes them indispensable across different sectors.
Q5: What is the advantage of using polymer PTC heating element?
A: Polymer PTC heating element is self-regulating, meaning its resistance increases as it heat up. This makes it energy-efficient and safe, as it automatically adjust power consumption to maintain the desired temperature without overheating. This feature makes it ideal for applications like electric radiators and heated seats.
For more information on heating elements and their applications, visit our detailed guide: Heating Elements Guide.
© 2024 DXM Blog. All rights reserved.
Author: Ivan Huang
Recommended for you
What Is Positive Temperature Coefficient? Expert Guide on PTC Thermistors
How to Find Impedance of a Capacitor: Guide for Professionals

how to calibrate rtd pt100?

Capacitor 104 Value: Essential Guide for Electronics Professionals

Positive Temperature Coefficient Heater: An Essential Guide of PTC Heater
What is an Electronic Ballast PTC Thermistor? Insights from DXM.
Customized Services
Free sample availability
You can contact our representative via email, fax or phone to specify the sample you need and provide your courier's account number (such as UPS, FedEx, DHL, TNT, etc.).. And we’ll send you samples free of charge through your courier by freight collection.
Price and Payment
Price
The price will be quoted in US dollars.
1) For small order quantities and small packing, normally our quotation is based on the ex-works price. The cargo will be delivered by courier after being finished normally.
2) For bulk orders and large volumes, normally our quotation is based on the FOB price. Please inform us of your destination seaport and estimated quantity, and our representative will quote you the C&F or CIF price accordingly. If you feel our freight is higher than your expectation, you can recommend your shipping company to us. Our principal is looking for a shipping company with a good reputation that offers competitive freight costs and can deliver your cargo promptly.
Do you offer bulk purchase discounts?
Yes, we offer bulk purchase discounts; the specific discount rate depends on the order quantity and cooperation method.
What’s the Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) and Minimum Order Amount (MOA)
MOQ: 10000PCS
Logistics
Is your logistics and distribution service reliable?
Yes, we cooperate with a number of well-known logistics companies to ensure the timeliness and reliability of logistics and distribution services and provide you with a satisfactory distribution experience.
You may also like

KTY83-110 Sensor with Silicon Glass Thermistor

Bracket Type NTC Thermal Sensor MF52X for Precise Temperature Measurement

Glass Thermistors MF58E for High-Precision Applications

High Precise NTC Sensors for Temperature Measurement and Control

WMZ12A 75S PTC Thermistors for Over-Current and Over-Load Protection

SMD Sensors: Advanced Temperature Sensing Excellence

Thermistor PTC MZ11 Series for Light Efficient Design

PTC Thermistors for Ballast Electronic and Energy Saving Lighting Intelligent Preheat Start MZ12 | DXM
Get in Touch
Discover premium thermistors, sensors, and resistors tailored to your needs.Our dedicated team of experts is available to assist with product selection, technical queries, and after-sales service. Contact us for custom solutions and experience exceptional customer support.
© 2025 DXM | All Rights Reserved.

 Scan QR Code
Scan QR Code
Scan QR Code
Whatsapp: +8618927361658
Shenzhen DXM Technology Co., Ltd.
DXM PTCNTC
Shenzhen DXM Technology Co., Ltd