Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) Thermistor is what: A Deep Dive
Explore the depths of the Negative Temperature Coefficient Thermistor with DXM. This article provides a comprehensive definition and insight into NTC, highlighting its significance and applications. Discover how an NTC thermistor works to improve temperature sensing and control. Join DXM on this deep dive into the wonders of negative temperature coefficient technology.
- Understanding the Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) and Its Significance
- What is a Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) Thermistor?
- Defining Negative Temperature Coefficient: Key Characteristics and Specifications
- Types of Negative Temperature Coefficient Thermistors and their Applications
- Understanding the Steinhart-Hart Equation for Precise Negative Temperature Coefficient Calculations
- FAQs about NTC Thermistors
- Conclusion

Understanding the Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) and Its Significance
The negative temperature coefficient (NTC) refers to materials whose resistance decreases as their temperature rises. This unique property is crucial in many applications, making it essential for professionals to define NTC and understand how it works. So, what is negative temperature coefficient? Essentially, NTC thermistors are devices that rely on this property to measure and control temperature accurately. The ability of an NTC thermistor to adjust its resistance with temperature makes it invaluable in industries like electronics, automotive, and HVAC systems.
Understanding negative temperature coefficient thermistors can enhance your ability to implement precise temperature control in diverse fields.
What is a Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) Thermistor?
A negative temperature coefficient thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance value decreases predictably as its temperature rises. This is in contrast to positive temperature coefficient (PTC) devices. The relationship between resistance (R) and temperature (T) in an NTC thermistor is typically described by the Steinhart-Hart equation, providing a highly accurate model for precise temperature measurement and control. This precise relationship is why NTC thermistors are so valuable. The core principle behind the negative temperature coefficient behavior lies in the material's semiconductor properties. As temperature increases, more electrons gain enough energy to jump into the conduction band, thus increasing conductivity and decreasing resistance.
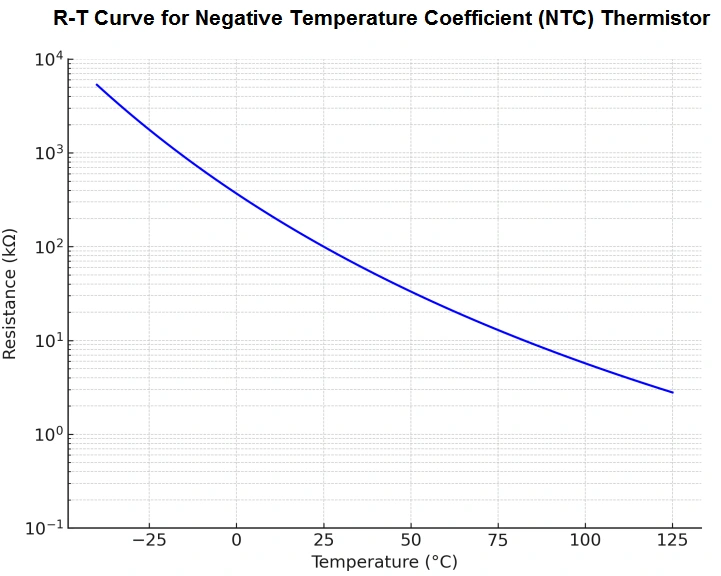
Defining Negative Temperature Coefficient: Key Characteristics and Specifications
When we define Negative Temperature Coefficient
, several key characteristics need clarification. Crucial specifications include:
* B Parameter (β): This parameter quantifies the sensitivity of the thermistor's resistance change with temperature. A higher β value indicates a more significant resistance decrease with temperature increase. Understanding the NTC thermistor's B parameter is critical for accurate temperature calculations.
* Resistance at 25°C (R25):This is the thermistor's resistance at a standard reference temperature of 25°C. This baseline value is essential for calibrating and interpreting measurements. The R25 value in conjunction with the B parameter is central to understanding a specific NTC device's properties.
* Tolerance: This specification indicates the acceptable variation in the thermistor's resistance value from the stated R25. It directly affects the accuracy of measurements derived from the NTC thermistor.
* Dissipation Constant: This parameter describes the thermistor's ability to dissipate heat. A higher dissipation constant indicates a greater ability to withstand higher power levels without significant self-heating, which could affect accuracy. Self-heating can significantly impact the negative temperature coefficient behavior.
* Temperature Range: This indicates the operational temperature range within which the thermistor’s negative temperature coefficient characteristics remain stable and reliable. Choosing the right NTC necessitates careful consideration of the operating environment.
Types of Negative Temperature Coefficient Thermistors and their Applications
We find NTC thermistors in diverse forms and applications, each designed to meet specific needs:
* Bead Thermistors:These are small, glass-encapsulated thermistors. Their small size makes them suitable for applications requiring high sensitivity and quick response times. They excel in compact temperature sensing.
* Chip Thermistors: These flat thermistors are suitable for surface mount technology (SMT). Their compact design makes them ideal for mass production and automated assembly processes.
* Rod Thermistors: These larger thermistors offer higher power dissipation capabilities, making them suitable for high-power applications or situations requiring robust construction. They are suitable for applications requiring greater heat dissipation capacity.
Applications leveraging the properties of NTC thermistors are extensive and include:
* Temperature Measurement and Control: This is perhaps the most widespread application. NTC thermistors are used in a myriad of devices, from simple thermometers to sophisticated industrial process control systems. Accurate temperature sensing is central to numerous applications.
* Thermal Protection: These sensors are often used as safety components, triggering shutdowns or alarms when temperatures exceed safe operating limits. Protecting equipment from overheating is a critical role for NTC components.
* Current Limiting: NTC thermistors are used to limit inrush current in electronic circuits. Their high resistance at low temperatures decreases as they heat up, gradually allowing current flow. This protection measure is vital in many electronic systems.
* Temperature Compensation: In some circuits, NTC thermistors are used to compensate for the temperature-dependent behavior of other components. This maintains stable circuit operation over a wider temperature range.
Understanding the Steinhart-Hart Equation for Precise Negative Temperature Coefficient Calculations
The Steinhart-Hart equation offers a highly accurate method for calculating temperature from the resistance of an NTC thermistor. It's expressed as:
1/T = A + B*ln(R) + C*(ln(R))^3
Where:
* T is the temperature in Kelvin
* R is the resistance of the NTC thermistor
* A, B, and C are coefficients specific to the particular NTC thermistor. These coefficients are supplied by the manufacturer.
This equation provides a far more precise relationship than simple linear approximations, particularly over wider temperature ranges. Mastering the use of this equation is vital for anyone working with Negative NTC thermistors for precise measurements.
FAQs about NTC Thermistors
Q: What is the difference between an NTC thermistor and a PTC thermistor?
A: An NTC thermistor's resistance decreases with increasing temperature, while a PTC thermistor's resistance increases with increasing temperature. This fundamental difference dictates their respective applications.
Q: How accurate are NTC thermistors?
A: The accuracy of an Negative Temperature Coefficient thermistor depends on several factors, including the thermistor's tolerance, the accuracy of the measurement circuitry, and the environmental conditions. High-precision NTC thermistors can offer accuracies of ±0.1°C or better.
Q: What are the limitations of NTC thermistors?
A: NTC thermistors are sensitive to self-heating, particularly at high currents. Their response time can also be slower than some other temperature sensors. Additionally, they are not typically suitable for extremely high-temperature applications.
Q: How do I choose the right Negative Temperature Coefficient thermistor for my application?
A: The selection process should consider factors such as the required temperature range, accuracy, power dissipation requirements, response time, and the physical size constraints. Consulting the manufacturer’s datasheets is crucial.
Conclusion
The negative temperature coefficient plays a vital role in many applications. Understanding how NTC thermistors behave is crucial for professionals in fields requiring precise temperature control. So, what is negative temperature coefficient? In simple terms, it's the characteristic of certain materials whose resistance decreases as their temperature increases. This property is invaluable for applications such as temperature sensing and circuit protection.
By grasping the key principles, parameters, and types of NTC thermistors, you can improve the accuracy and reliability of temperature-sensitive systems. These thermistors offer versatility and precision across various industries. Whether you're measuring temperature or ensuring thermal protection, Negative Temperature Coefficient thermistors are essential for efficient and innovative solutions. Explore their benefits to enhance your projects and make smarter choices in temperature control.
© 2025 DXM Blog. All rights reserved.
Author: Ivan Huang
Recommended for you

Water Temperature Sensor: The Key to Engine Health and Efficiency

Lightning Surge Protection Varistor: Essential for Protecting Your Electrical Systems

Water Temp Sensor: How to Test it for Reliable Performance?
Capacitor Impedance: Calculation Guide & FAQs

Temperature Probe Sensor: A Comprehensive Guide

Termistor NTC: What Does a Thermistor Do?
Price and Payment
What’s the Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) and Minimum Order Amount (MOA)
MOQ: 10000PCS
Are invoices provided?
Yes, we provide legal invoices that can be used for reimbursement and accounting records.
Price
The price will be quoted in US dollars.
1) For small order quantities and small packing, normally our quotation is based on the ex-works price. The cargo will be delivered by courier after being finished normally.
2) For bulk orders and large volumes, normally our quotation is based on the FOB price. Please inform us of your destination seaport and estimated quantity, and our representative will quote you the C&F or CIF price accordingly. If you feel our freight is higher than your expectation, you can recommend your shipping company to us. Our principal is looking for a shipping company with a good reputation that offers competitive freight costs and can deliver your cargo promptly.
Logistics
How to track my order?
You can track your order through our official website or the order number provided and learn about the logistics status and delivery progress of your order at any time.
Customized Services
Free sample availability
You can contact our representative via email, fax or phone to specify the sample you need and provide your courier's account number (such as UPS, FedEx, DHL, TNT, etc.).. And we’ll send you samples free of charge through your courier by freight collection.
You may also like

KTY83-110 Sensor with Silicon Glass Thermistor

Bracket Type NTC Thermal Sensor MF52X for Precise Temperature Measurement

Glass Thermistors MF58E for High-Precision Applications

High Precise NTC Sensors for Temperature Measurement and Control

WMZ12A 75S PTC Thermistors for Over-Current and Over-Load Protection

SMD Sensors: Advanced Temperature Sensing Excellence

Thermistor PTC MZ11 Series for Light Efficient Design

PTC Thermistors for Ballast Electronic and Energy Saving Lighting Intelligent Preheat Start MZ12 | DXM
Get in Touch
Discover premium thermistors, sensors, and resistors tailored to your needs.Our dedicated team of experts is available to assist with product selection, technical queries, and after-sales service. Contact us for custom solutions and experience exceptional customer support.
© 2024 DXM | Designed by gooeyun

 Scan QR Code
Scan QR Code
Scan QR Code
Whatsapp: +8618927361658
Shenzhen DXM Technology Co., Ltd.
DXM PTCNTC
Shenzhen DXM Technology Co., Ltd