PTC Meaning: Unveiling Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistor
Discover PTC meaning in our latest article on DXM. Dive into the world of Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) elements, commonly known as Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistor. These innovative components play a crucial role in modern electronics by providing reliable overcurrent protection. Our comprehensive guide offers insights into their functionality and applications. Enhance your knowledge with DXM’s expert analysis on PTC elements and their impact on technology today. Perfect for engineers and tech enthusiasts seeking detailed information.
- 1. Introduction: Understanding the PTC Meaning and Its Significance
- 2. Operating Principles: How PTC Elements Work
- 2.1 Positive Temperature Coefficient: PTC meaning Effect
- 2.2 Self-Heating Mode: A Key Functionality
- 2.3 Sensing Mode: Precision without Self-Heating
- 3. Key Characteristics: Definition of PTC Elements
- 3.1 Resistance-Temperature Relationship: A Nonlinear Behavior
- 3.2 Dissipation Constant: Managing Heat in PTC Elements
- 3.3 Rated Current and Voltage: Ensuring Safe Operation
- 4. Manufacturing Process: How PTC Elements are Made
- 4.1 Materials Used in Positive Temperature-Sensitive Resistor Production
- 4.2 Manufacturing Steps: Precision in Production
- 5. Applications: Real-World Uses of PTC Elements
- 5.1 Ensuring Circuit Safety with Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistors
- 5.2 Time-Delay Circuits: Leveraging Self-Heating
- 5.3 Motor Startup Windings: Controlled Current Flow
- 6. Conclusion: Unlocking the Full Potential of Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistors
- Q&A: Deepening Understanding of PTC Meaning and Applications
- Q: How do Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistor differ from NTC thermistors?
- Q: What are the main applications of Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistor?
- Q: How do manufacturers ensure Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistor meet their specifications?

Understanding the PTC meaning is crucial for electronics enthusiasts and professionals alike. PTC stands for Positive Temperature Coefficient, a key characteristic of certain thermistors. This Temperature-Dependent Resistor plays a vital role in modern circuits, offering unique properties for temperature sensing and protection. Let's explore the definition of PTC elements and their applications.
1. Introduction: Understanding the PTC Meaning and Its Significance
The PTC meaning in electronics refers to components whose resistance increases with temperature. This behavior defines PTC Elements and sets them apart from other Resistors. To define PTC elements fully, we must explore their characteristics and applications in electronic circuits.
Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistor is crucial in many electronic systems. Their unique properties make them ideal for temperature sensing, overcurrent protection, and self-regulating heating applications. Understanding the PTC meaning is essential for designing efficient and safe electronic devices.
2. Operating Principles: How PTC Elements Work
To fully grasp the PTC meaning, we must understand the operating principles of these devices. The behavior of Temperature-sensitive resistor is rooted in material physics and electrical properties.
2.1 Positive Temperature Coefficient: PTC meaning Effect
The core lies in the positive temperature coefficient of resistance. As temperature rises, the resistance increases. This behavior is central to how we define Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistor and its applications.
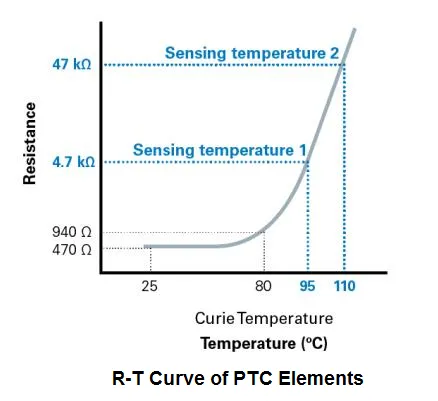
2.2 Self-Heating Mode: A Key Functionality
Self-heated mode is a key aspect of the PTC meaning in many applications. In this mode, current flow causes internal heating in PTC Elements, leading to increased resistance and current limitation.
2.3 Sensing Mode: Precision without Self-Heating
The sensing mode demonstrates another facet of the PTC meaning. In this mode, Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistor measures ambient temperature without significant self-heating, showcasing its versatility.
3. Key Characteristics: Definition of PTC Elements
To fully understand the definition of Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistor, we must examine the key characteristics of these devices. These properties are essential to the functionality in various applications.
3.1 Resistance-Temperature Relationship: A Nonlinear Behavior
The resistance-temperature relationship is central to the PTC meaning. This nonlinear relationship defines how Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistor responds to temperature changes, influencing its performance in circuits.
3.2 Dissipation Constant: Managing Heat in PTC Elements
The dissipation constant is crucial when we define Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistor for specific uses. It affects how quickly they can dissipate heat, influencing their response time and self-heating characteristics.
3.3 Rated Current and Voltage: Ensuring Safe Operation
Rated current and voltage are important parameters in the PTC meaning. These ratings define the operational limits and are crucial for proper circuit design and safety.
4. Manufacturing Process: How PTC Elements are Made
The manufacturing process is an integral part of the PTC meaning in practical applications. The production of Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistor involves several key steps that determine their final properties.
4.1 Materials Used in Positive Temperature-Sensitive Resistor Production
The materials used in Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistor are crucial to their behavior. Ceramic materials like barium titanate and conductive polymers are commonly used to create devices that embody the PTC meaning.
4.2 Manufacturing Steps: Precision in Production
The manufacturing steps are key to producing Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistor that meet specific requirements. These steps, from material preparation to final testing, ensure that the produced devices exhibit the desired PTC meaning in their behavior.
5. Applications: Real-World Uses of PTC Elements
The applications of Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistor showcase the practical aspects of the PTC meaning. These uses demonstrate how the unique properties of these devices translate into real-world solutions.
5.1 Ensuring Circuit Safety with Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistors
Overcurrent protection is a key function of the Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistor in circuit safety. Acting as self-resetting fuses, these resistors prevent circuit damage from excessive current. Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistors increase resistance as temperatures rise, effectively limiting current flow. This built-in protection reduces the need for manual intervention in circuit maintenance.
By integrating Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistors, circuits gain efficient and reliable protection. This technology meets high safety standards and ensures long-term operational stability, making it a preferred choice for modern electronic systems.
5.2 Time-Delay Circuits: Leveraging Self-Heating
Time-delay circuits benefit from the self-heating properties inherent in the PTC meaning. This application showcases how Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistor can be used for timing and sequencing in electronic systems.
5.3 Motor Startup Windings: Controlled Current Flow
Motor startup applications to provide initial high current and subsequent current limiting. This use demonstrates the versatility of Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistor in power applications.
6. Conclusion: Unlocking the Full Potential of Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistors
Understanding the PTC meaning is essential for maximizing the benefits of these components. Positive Temperature-sensitive resistor is vital in modern electronics, providing solutions for temperature sensing, circuit protection, and self-regulation. As technology advances, the role of these devices will continue to grow, impacting numerous applications.
The future of thermistors is bright, with ongoing research into new materials and manufacturing methods.
Q&A: Deepening Understanding of PTC Meaning and Applications
PTC stands for Positive Temperature Coefficient. This is the core in the context of resistors, indicating that the resistance of these devices increases with temperature.
Q: How do Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistor differ from NTC thermistors?
A: The key difference lies in their temperature-resistance relationship,which implies increasing resistance with temperature, while NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient) thermistors exhibit decreasing resistance as temperature rises.
Q: What are the main applications of Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistor?
A: Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistor finds applications in overcurrent protection, time-delay circuits, motor startup windings, and temperature sensing and control. These applications leverage various aspects of the PTC meaning in practical scenarios.
Q: How do manufacturers ensure Positive Temperature-Dependent Resistor meet their specifications?
A: Manufacturers follow a precise production process aligned with the desired characteristics. This includes careful material selection, controlled manufacturing steps, and rigorous testing to ensure each device meets the required performance specifications.
Recommended for you

Water Temperature Sensor: The Key to Engine Health and Efficiency

Lightning Surge Protection Varistor: Essential for Protecting Your Electrical Systems

Water Temp Sensor: How to Test it for Reliable Performance?
Capacitor Impedance: Calculation Guide & FAQs

Temperature Probe Sensor: A Comprehensive Guide

Termistor NTC: What Does a Thermistor Do?
Price and Payment
Payment Terms
There are a number of different payment methods that can be used when you deal with us. Two are mostly used: T/T payment in advance for small values and irrevocable L/C at sight for large values.
Logistics
Can I change my shipping address?
Yes, you can contact our customer service team to modify the delivery address before order confirmation to ensure that the order can be accurately delivered to the address you specify.
Is your logistics and distribution service reliable?
Yes, we cooperate with a number of well-known logistics companies to ensure the timeliness and reliability of logistics and distribution services and provide you with a satisfactory distribution experience.
Customized Services
Free sample availability
You can contact our representative via email, fax or phone to specify the sample you need and provide your courier's account number (such as UPS, FedEx, DHL, TNT, etc.).. And we’ll send you samples free of charge through your courier by freight collection.
Can I customize (OEM) the product?
Yes. You can customize the product with DXM. Our R&D and production technology have already reached an advanced world level, and we can provide qualified OEM service for global customers.Please specify your requirements to our representative or send samples to our factory office, and we will confirm your details.
You may also like

KTY83-110 Sensor with Silicon Glass Thermistor

Bracket Type NTC Thermal Sensor MF52X for Precise Temperature Measurement

Glass Thermistors MF58E for High-Precision Applications

High Precise NTC Sensors for Temperature Measurement and Control

WMZ12A 75S PTC Thermistors for Over-Current and Over-Load Protection

SMD Sensors: Advanced Temperature Sensing Excellence

Thermistor PTC MZ11 Series for Light Efficient Design

PTC Thermistors for Ballast Electronic and Energy Saving Lighting Intelligent Preheat Start MZ12 | DXM
Get in Touch
Discover premium thermistors, sensors, and resistors tailored to your needs.Our dedicated team of experts is available to assist with product selection, technical queries, and after-sales service. Contact us for custom solutions and experience exceptional customer support.
© 2024 DXM | Designed by gooeyun

 Scan QR Code
Scan QR Code
Scan QR Code
Whatsapp: +8618927361658
Shenzhen DXM Technology Co., Ltd.
DXM PTCNTC
Shenzhen DXM Technology Co., Ltd