NTC Resistor: The Future of Temperature Control Technology
Explore the future of temperature control technology with DXM's NTC Resistor. Our Negative Temperature Coefficient Resistor offers precision and reliability, crucial for modern applications in various industries. Designed to optimize performance, these resistors ensure responsive and accurate temperature monitoring. Trust DXM for cutting-edge solutions that enhance efficiency and safety. Delve into the advantages of our NTC Resistor and elevate your systems with superior components. Embrace innovation and stay ahead in a rapidly evolving technological landscape.
- Understanding NTC Resistor: Core Principles and Functionality
- Key Characteristics of NTC Resistor
- Working Principle: The Science Behind NTC Resistor
- Mathematical Models for NTC Resistor Behavior
- Types and Construction: Diverse Forms of NTC Resistor
- 1. Bead Type NTC Thermistor
- 2. Disk and Chip NTC Thermistor
- 3. Glass-Encapsulated NTC Thermistor
- Frequently Asked Questions About NTC Resistor
- Q: What exactly does NTC mean in NTC resistor?
- Q: How do NTC resistors differ from standard resistors?
- Q: What are the primary applications of NTC thermistors?
- Q: Can NTC resistor be used in high-temperature environments?
- Q: What advantages do NTC resistors have over other temperature sensors?
- Q: How accurate is NTC resistor in temperature measurement?
- Q: Are there any limitations to using NTC resistors?
- Q: How do I choose the right NTC resistor for my application?
In the realm of electronic components, NTC resistor stands out as essential elements for precise temperature measurement and control. This Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) Resistor, also known as NTC thermistor, plays a pivotal role across industries due to their unique properties and versatile applications. This comprehensive guide delves into the characteristics, working principles, and advantages of NTC resistor, exploring how they revolutionize temperature sensing technology.
Understanding NTC Resistor: Core Principles and Functionality
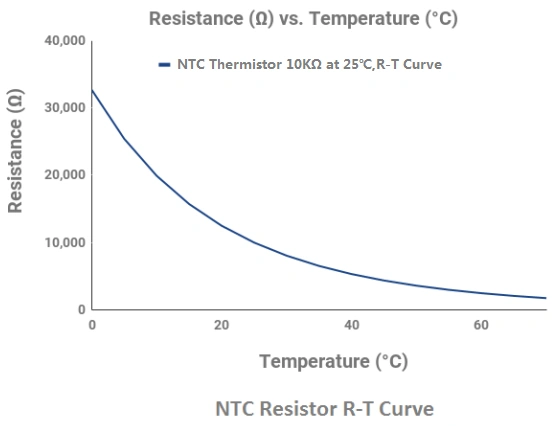
NTC resistor is specialized electronic components engineered to alter their resistance in response to temperature changes. Unlike standard resistors, NTC devices exhibit a decrease in resistance as temperature rises, hence the term "negative temperature coefficient." This inverse relationship between temperature and resistance makes NTC resistor invaluable in precise temperature measurement and control systems across various applications.
Key Characteristics of NTC Resistor
- Negative Temperature Coefficient: The defining feature of NTC resistor is their negative temperature coefficient. As ambient temperature increases, the resistance of the NTC device drops significantly. This behavior contrasts with positive temperature coefficient (PTC) devices, making NTC resistor ideal for temperature sensing applications in diverse environments.
- High Sensitivity: NTC thermistors boast exceptional sensitivity to temperature fluctuations. Typically, they exhibit a sensitivity coefficient ranging from -3% to -6% per degree Celsius. This high sensitivity enables precise temperature measurements, even in applications requiring detection of minute thermal variations.
- Wide Operating Range: Most NTC resistor functions effectively within a temperature span of -55°C to 200°C. However, specialized NTC thermistor can operate in even more extreme conditions, making them suitable for a broad spectrum of industrial and scientific applications where temperature monitoring is critical.
Working Principle: The Science Behind NTC Resistor
The operation of NTC resistors relies on the fundamental relationship between temperature and electrical resistance in semiconductor materials. As temperature rises, more charge carriers are released in the semiconductor, leading to decreased resistance. This non-linear relationship is often approximated using various mathematical models to ensure accurate temperature readings across different scenarios.
Mathematical Models for NTC Resistor Behavior
Several equations are employed to describe the behavior of NTC resistors, each offering different levels of accuracy and complexity:
- First-order approximation: A simplified model for quick calculations in less demanding applications.
- Steinhart-Hart equation: A more complex and accurate model for precise temperature measurements, widely used in scientific and high-precision industrial settings.
- Beta parameter equation: Commonly used in industry for its balance of accuracy and simplicity, making it a popular choice for a wide range of applications.
Types and Construction: Diverse Forms of NTC Resistor
NTC resistor comes in various forms, each designed for specific applications and environmental conditions. Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the right NTC thermistor for your project:
1. Bead Type NTC Thermistor
Bead type NTC resistors are among the smallest available thermistors.
They consist of a tiny bead of semiconductor material suspended between two fine wires.Key features include:
- Rapid response times due to small size
- Ideal for applications requiring quick temperature sensing
- Commonly used in airflow sensors and medical devices
-
2. Disk and Chip NTC Thermistor
Disk and chip NTC resistor is manufactured by pressing and sintering semiconductor material into flat disks or rectangular chips.
Their characteristics include:
- Excellent stability over time
- Suitable for surface mount technology (SMT) applications
- Widely used in temperature compensation circuits and industrial control systems
-
3. Glass-Encapsulated NTC Thermistor

Glass-sealed NTC resistor is designed for high-temperature applications and harsh environments. Notable features:
- Enhanced stability at high temperatures
- Protection against harsh chemicals and moisture
- Ideal for automotive and industrial applications where reliability is crucial
Frequently Asked Questions About NTC Resistor
Q: What exactly does NTC mean in NTC resistor?
A: NTC stands for Negative Temperature Coefficient. This term describes the fundamental property of these resistors: their resistance decreases as temperature increases. This inverse relationship between temperature and resistance is what makes NTC resistor ideal for temperature sensing and measurement applications.Q: How do NTC resistors differ from standard resistors?
A: Unlike standard resistors which maintain a relatively constant resistance across a wide temperature range, NTC resistors are designed to change their resistance significantly with temperature variations. Standard resistors aim for stability, while NTC resistors leverage their temperature sensitivity for measurement and control applications.Q: What are the primary applications of NTC thermistors?
A: NTC thermistors find wide use in various fields: 1. Temperature measurement and control in HVAC systems 2. Overtemperature protection in electronic devices 3. Temperature compensation in circuit designs 4. Battery temperature monitoring in electric vehicles 5. Medical equipment for precise body temperature sensing 6. Industrial process control where temperature monitoring is criticalQ: Can NTC resistor be used in high-temperature environments?
A: Yes, certain types of NTC resistors, particularly glass-encapsulated models, are designed for high-temperature applications. Some specialized NTC thermistors can operate effectively at temperatures up to 300°C or even higher. However, it's crucial to select the right type of NTC resistors based on the specific temperature range of your application.Q: What advantages do NTC resistors have over other temperature sensors?
A: NTC resistors offer several benefits: 1. High sensitivity to temperature changes 2. Fast response times due to their small size 3. Cost-effectiveness compared to many other sensor types 4. Wide temperature range capability 5. Simplicity in circuit design and implementation 6. Durability and long-term stability when properly selected and usedQ: How accurate is NTC resistor in temperature measurement?
A: The accuracy of NTC resistor can vary depending on the specific model and how they're implemented. High-quality NTC thermistors can achieve accuracies of ±0.1°C or better in controlled conditions. However, factors such as self-heating, thermal mass, and the accuracy of the associated circuitry can affect overall measurement precision. Proper calibration and implementation are key to achieving high accuracy.Q: Are there any limitations to using NTC resistors?
A: While NTC resistors are versatile, it does have some limitations: 1. Non-linear resistance-temperature relationship, requiring linearization for precise measurements 2. Potential for self-heating errors if not properly managed 3. Sensitivity to mechanical stress, which can affect accuracy 4. Limited interchangeability without individual calibration 5. Potential for long-term drift in some environments Understanding these limitations is crucial for designing effective temperature measurement systems.Q: How do I choose the right NTC resistor for my application?
A: Selecting the appropriate NTC resistor involves considering several factors:Recommended for you

Degausser and Degaussing TV Resistor: A Complete Guide

Temperature Probe: A Comprehensive Guide

Resistance Temperature Detector Price: A Comprehensive Guide

Electrical Components International: Top Electrical Component Manufacturer DXM

PTC Sensor: Understanding & Applications
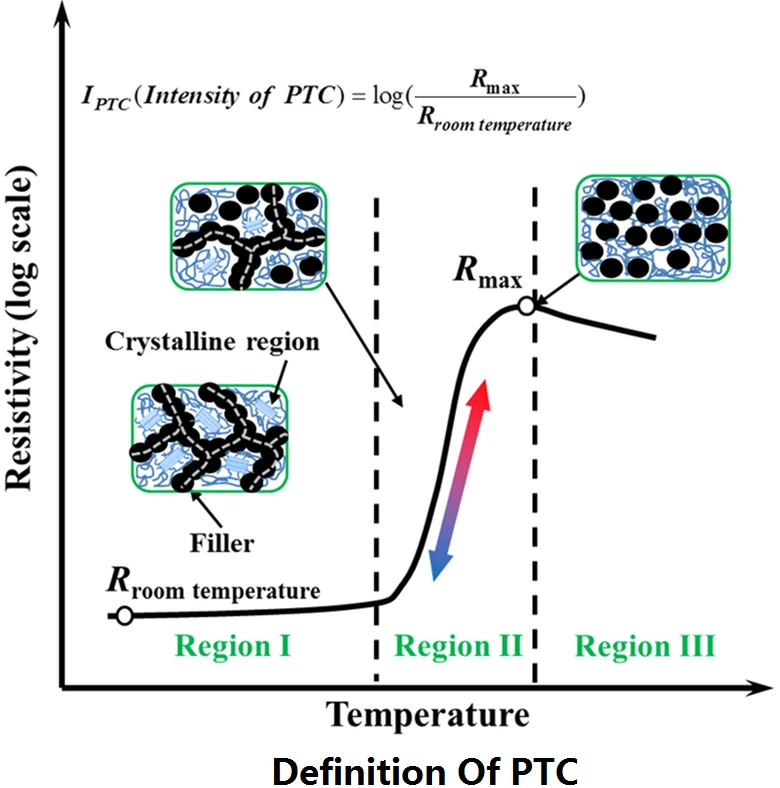
Definition of PTC: Positive Temperature Coefficient Explained
Logistics
Does your product support global logistics and distribution?
Yes, our products support global logistics and distribution services, and you can receive our products anytime and anywhere.
Does it support express delivery?
Yes, we support express delivery services. You can choose different delivery methods according to your needs, including ordinary express delivery and expedited express delivery.
Price and Payment
Are invoices provided?
Yes, we provide legal invoices that can be used for reimbursement and accounting records.
Payment Terms
There are a number of different payment methods that can be used when you deal with us. Two are mostly used: T/T payment in advance for small values and irrevocable L/C at sight for large values.
Customized Services
Custom-made sample/order
SHENZHEN DXM TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. are structured by high-tech talents from famous university
in China and accompanied with a batch of ceramic-sensitive components experts and technology
specialist, have powerful R&D and technology capabilities.DXM is one of a few manufacturers
master core production technology of ceramic-sensitive components in the world.
Samples and orders can be custom-made per customer’s requirements, as below:
1. Application environment of product
2. Required specifications or technical parameters
3. Reference sample
4. Reference drawing
You may also like

KTY83-110 Sensor with Silicon Glass Thermistor

Bracket Type NTC Thermal Sensor MF52X for Precise Temperature Measurement

Glass Thermistors MF58E for High-Precision Applications

High Precise NTC Sensors for Temperature Measurement and Control

WMZ12A 75S PTC Thermistors for Over-Current and Over-Load Protection

SMD Sensors: Advanced Temperature Sensing Excellence

Thermistor PTC MZ11 Series for Light Efficient Design

PTC Thermistors for Ballast Electronic and Energy Saving Lighting Intelligent Preheat Start MZ12 | DXM
Get in Touch
Discover premium thermistors, sensors, and resistors tailored to your needs.Our dedicated team of experts is available to assist with product selection, technical queries, and after-sales service. Contact us for custom solutions and experience exceptional customer support.
© 2024 DXM | Designed by gooeyun

 Scan QR Code
Scan QR Code
Scan QR Code
Whatsapp: +8618927361658
Shenzhen DXM Technology Co., Ltd.
DXM PTCNTC
Shenzhen DXM Technology Co., Ltd